|
Trauma Series - Part 3 of 7
Experiencing trauma can have profound effects on an individual's mental, emotional, and physical well-being. It's important to recognize and understand the various symptoms associated with trauma to provide appropriate support and facilitate healing. In this blog post, we will delve into some common trauma symptoms to include addiction, avoidance, dissociation, flashbacks, hypervigilance, memory difficulties, mood swings, pain or illness, sleep problems, and suicidal ideation. By shedding light on these symptoms, we aim to promote awareness, empathy, and resilience in the face of trauma.
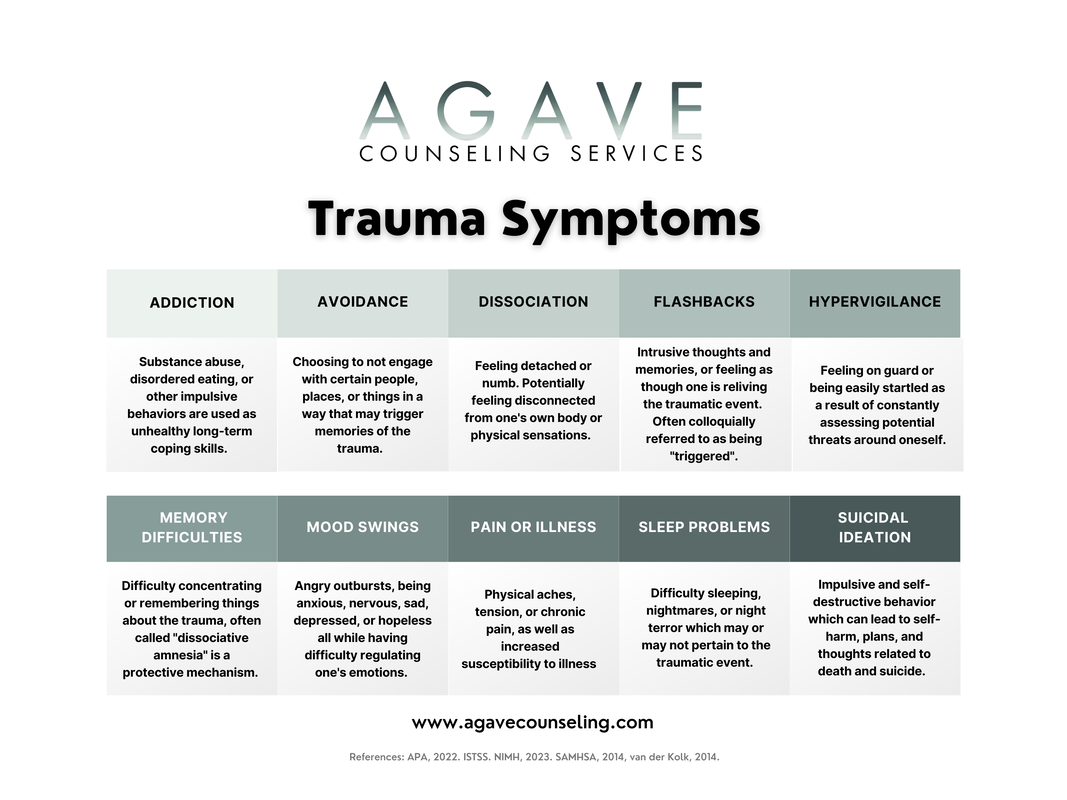
1. Addiction: Trauma can be a triggering factor for addiction, as individuals may turn to substances or behaviors to cope with emotional pain and distress (SAMHSA, 2014; ISTSS). Recognizing the link between trauma and addiction is crucial in seeking appropriate care. Engaging in therapy, support groups, and holistic approaches can aid in addressing underlying trauma while developing healthy coping mechanisms. 2. Avoidance: Avoidance is a common response to trauma, where individuals consciously or unconsciously try to steer clear of people, places, or situations that trigger distressing memories or emotions (APA, 2022). While avoidance may provide temporary relief, it can hinder the healing process long-term. Gradual exposure to triggers with the guidance of a therapist can empower individuals to reclaim control over their lives. 3. Dissociation: Dissociation is a defense mechanism that involves feeling disconnected from oneself, the environment, or the present moment (van der Kolk, 2014). It can manifest as a sense of detachment, amnesia, or feeling as though life is unreal (NIMH, 2023). Seeking therapy and engaging in grounding techniques can help individuals reconnect with their emotions, experiences, and regain a sense of stability. 4. Flashbacks: A flashback is the vivid and intrusive re-experiencing of a traumatic event, often making individuals feel as though they are reliving the trauma (APA, 2022). They can be triggered by sensory cues or emotional reminders. Coping strategies such as grounding techniques, deep breathing, and seeking professional support can help manage and process flashbacks effectively. 5. Hypervigilance: Hypervigilance refers to a heightened state of alertness and sensitivity to potential threats, often leading individuals to be constantly on guard (APA, 2022). This hypervigilance is a natural response to trauma, designed to protect against future harm. However, it can result in chronic anxiety and exhaustion. Practicing relaxation techniques, self-care, and seeking therapy can assist in managing hypervigilance and restoring a sense of safety. 6. Memory Difficulties: Trauma can impact memory processing, leading to difficulties with concentration, short-term memory, and recall (APA, 2022). These challenges can affect daily functioning and relationships. Strategies such as creating routines, using memory aids, and practicing mindfulness can help improve memory and cognitive function over time. 7. Mood Swings: Mood swings are common among individuals who have experienced trauma, with emotions fluctuating between extreme highs and lows (APA, 2022). These mood swings can be challenging to manage and may impact personal and professional relationships. Engaging in therapy, practicing self-care, and learning healthy emotion regulation techniques can aid in stabilizing mood fluctuations. 8. Pain or Illness: Physical symptoms such as chronic pain or unexplained illnesses can be associated with trauma (SAMHSA, 2014). Trauma can manifest in the body, leading to discomfort and distress. Integrating a holistic approach, which may include therapy, medication, relaxation techniques, and alternative therapies, can help alleviate physical symptoms and promote overall well-being. 9. Sleep Problems: Sleep disturbances, including insomnia, nightmares, and night terrors, are common among individuals who have experienced trauma (NIMH, 2023). Establishing a consistent sleep routine, practicing relaxation techniques before bed, and seeking therapy to address trauma-related sleep disturbances can help improve sleep quality and promote restorative rest. 10. Suicidal Ideation: Trauma can significantly impact an individual's mental health, leading to feelings of hopelessness and thoughts of self-harm or suicide (APA, 2022). It is crucial to take suicidal ideation seriously and seek immediate professional help. Therapeutic interventions, support systems, and safety planning can provide essential support for those experiencing such thoughts and promote resilience. In conclusion, trauma can leave deep imprints on individuals, affecting a multitude of aspects within their lives. By recognizing and understanding common trauma symptoms, such as the aforementioned, we can foster empathy and create a supportive environment for healing. Additionally, it is essential to seek professional help, build a strong support network, and practice self-care as part of the journey toward healing and recovery. References 1. American Psychiatric Association. (2022). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (5th ed., text rev.). https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.books.9780890425787 2. Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder. (2023, May). National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH). https://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/topics/post-traumatic-stress-disorder-ptsd/index.shtml 3. Trauma-Informed Care in Behavioral Health Services. (2014). Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA). https://store.samhsa.gov/sites/default/files/d7/priv/sma14-4816.pdf 4. Traumatic Stress and Substance Abuse Problems. (n.d.). International Society for Traumatic Stress Studies (ISTSS). Retrieved from https://istss.org/ISTSS_Main/media/Documents/ISTSS_TraumaStressandSubstanceAbuseProb_English_FNL.pdf 5. van der Kolk, B. A. (2014). The body keeps the score: Brain, mind, and body in the healing of trauma. Viking.
0 Comments
|
ExtrasFreebies & E-Courses ThemesRecent posts |
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed